- About
- Issues
-
-
Issues
-
- AI Imperative 2030China is aggressively pursuing AI development using a whole-of-government, industrial collaboration policy. The authoritarian regime in Beijing has closed the gap with the United States in terms of AI capabilities, with an increasingly sophisticated approach to the elimination of barriers between civilian research and commercial sectors and military and defense industrial sectors.
- American Competitiveness & Economic DiplomacyA look at the strength of America’s business and trade relations undergirds its competitiveness abroad. In the global marketplace of ideas, the United States must lead in its business, infrastructure, and innovation if it’s to thrive.
- ARCTICArctic sea ice is melting as the climate changes, making the region more navigable, and opening up the area to resource competition, trade, and more opportunities for conflict.
- Asymmetric Operations
- China Policy & Strategic CompetitionA wide ranging look at U.S. strategic competition with China and the ways in which it affects American policy and interests. This includes strategic competition over global influence, economic markets, military capacity, and technological advancement.
- Climate SecurityClimate change is a core component of U.S. national security in the 21st century that challenges military readiness. It exacerbates existing threats, risks, and hazards while simultaneously creating new ones. These climate risks act as an accelerant of instability and a threat multiplier, especially in fragile states.
- Cuba Engagement
- Energy SecurityEnergy refers to everything from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources and the infrastructure that underpins them, like the national grid and energy storage. Energy security is a function of availability, consistent access, and predictable pricing. Energy security is not energy independence.
-
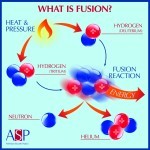
- Fusion EnergyFusion is energy released by forcing atomic nuclei together—the same process that powers the sun. The primary fuel for fusion is derived from ordinary water. Electricity produced from fusion will be safe and clean.
- Latin America and the CaribbeanLatin America and the Caribbean (LAC) face a number of critical security challenges. Democratic backsliding has accelerated across the region, weakening political systems already weighed down by corruption, impunity, and inequality. Trends in the LAC region impact U.S. national security.
- Maritime SecurityThe issues related to maritime security often involve national boundary disputes, but also include include illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing and transnational organized crimes: piracy; armed robbery at sea; human, drug, and weapons trafficking; and marine pollution.
- National Security & SpaceCompetition in space is heating up and a new space race is beginning. While space has been and can continue to be an area for scientific cooperation, there is a growing risk of conflict developing between space-faring nations.
- National Security StrategyAmerica’s national security is affected by a variety of factors, including diplomatic relations, conflict between countries, the evolving nature of cyber security, the budgetary process, and even military recruiting efforts. ASP provides a wide-ranging look at the full spectrum of national security issues.
- Nuclear SecurityNuclear weapons proliferation is increasing and nascent nuclear powers pose an increasing threat. Diplomatic efforts should be aimed at reducing these threats. A 21st century U.S. nuclear strategy should provide a strong, effective deterrent aimed at reducing wasteful spending on weapons that are inherently unusable.
- Public DiplomacyThe relationships America builds with foreign publics are essential to building consensus around the ideals and principles that should guide a 21st century vision for security. What can the United States learn from overseas perceptions in order to achieve its policy goals?
- US-Russia RelationshipThe U.S.-Russia relationship is fraught with challenges and difficulties. The United States needs to push back against Russian aggression while working to maintain the essentials of a relationship that reduces risks for both sides.
-
-
- Blog
- Events
-
-
Events
-
-
- Reports
- Media Inquiries
- Donate

- About
- Issues
-
-
Issues
-
- AI Imperative 2030China is aggressively pursuing AI development using a whole-of-government, industrial collaboration policy. The authoritarian regime in Beijing has closed the gap with the United States in terms of AI capabilities, with an increasingly sophisticated approach to the elimination of barriers between civilian research and commercial sectors and military and defense industrial sectors.
- American Competitiveness & Economic DiplomacyA look at the strength of America’s business and trade relations undergirds its competitiveness abroad. In the global marketplace of ideas, the United States must lead in its business, infrastructure, and innovation if it’s to thrive.
- ARCTICArctic sea ice is melting as the climate changes, making the region more navigable, and opening up the area to resource competition, trade, and more opportunities for conflict.
- Asymmetric Operations
- China Policy & Strategic CompetitionA wide ranging look at U.S. strategic competition with China and the ways in which it affects American policy and interests. This includes strategic competition over global influence, economic markets, military capacity, and technological advancement.
- Climate SecurityClimate change is a core component of U.S. national security in the 21st century that challenges military readiness. It exacerbates existing threats, risks, and hazards while simultaneously creating new ones. These climate risks act as an accelerant of instability and a threat multiplier, especially in fragile states.
- Cuba Engagement
- Energy SecurityEnergy refers to everything from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources and the infrastructure that underpins them, like the national grid and energy storage. Energy security is a function of availability, consistent access, and predictable pricing. Energy security is not energy independence.
-
- Fusion EnergyFusion is energy released by forcing atomic nuclei together—the same process that powers the sun. The primary fuel for fusion is derived from ordinary water. Electricity produced from fusion will be safe and clean.
- Latin America and the CaribbeanLatin America and the Caribbean (LAC) face a number of critical security challenges. Democratic backsliding has accelerated across the region, weakening political systems already weighed down by corruption, impunity, and inequality. Trends in the LAC region impact U.S. national security.
- Maritime SecurityThe issues related to maritime security often involve national boundary disputes, but also include include illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing and transnational organized crimes: piracy; armed robbery at sea; human, drug, and weapons trafficking; and marine pollution.
- National Security & SpaceCompetition in space is heating up and a new space race is beginning. While space has been and can continue to be an area for scientific cooperation, there is a growing risk of conflict developing between space-faring nations.
- National Security StrategyAmerica’s national security is affected by a variety of factors, including diplomatic relations, conflict between countries, the evolving nature of cyber security, the budgetary process, and even military recruiting efforts. ASP provides a wide-ranging look at the full spectrum of national security issues.
- Nuclear SecurityNuclear weapons proliferation is increasing and nascent nuclear powers pose an increasing threat. Diplomatic efforts should be aimed at reducing these threats. A 21st century U.S. nuclear strategy should provide a strong, effective deterrent aimed at reducing wasteful spending on weapons that are inherently unusable.
- Public DiplomacyThe relationships America builds with foreign publics are essential to building consensus around the ideals and principles that should guide a 21st century vision for security. What can the United States learn from overseas perceptions in order to achieve its policy goals?
- US-Russia RelationshipThe U.S.-Russia relationship is fraught with challenges and difficulties. The United States needs to push back against Russian aggression while working to maintain the essentials of a relationship that reduces risks for both sides.
-
-
- Blog
- Events
-
-
Events
-
-
- Reports
- Media Inquiries
- Donate